Uterine Fibroid Treatment.
Introduction
From Menstruation to Menopause, women’s health undergoes changes. With the advancement in research and medicine, women still face unique challenges in maintaining their health. Some of health issues are yet to be understood. In this article, we will give a thorough explanation of a common health challenge among women. UTERINE FIBROID.
What is Uterine fibroid?
Uterine fibroid also referred as leiomyomas, are non – cancerous growth that develop in and around the uterus. The World Health Organization (WHO) defined Uterine fibroid as a benign tumor of the uterus, composed of smooth muscle and fibroid tissue.
On the part the NICHD,( National Institute of Child Health and Human Development) it is non-cancerous growth that develops in and around the Uterus composed of muscle fibrous tissue.
Uterine fibroid is the most common and misunderstood health issue in women. Statically, fibroid affects 70-80% of women at the age 50%. It is common among black women.
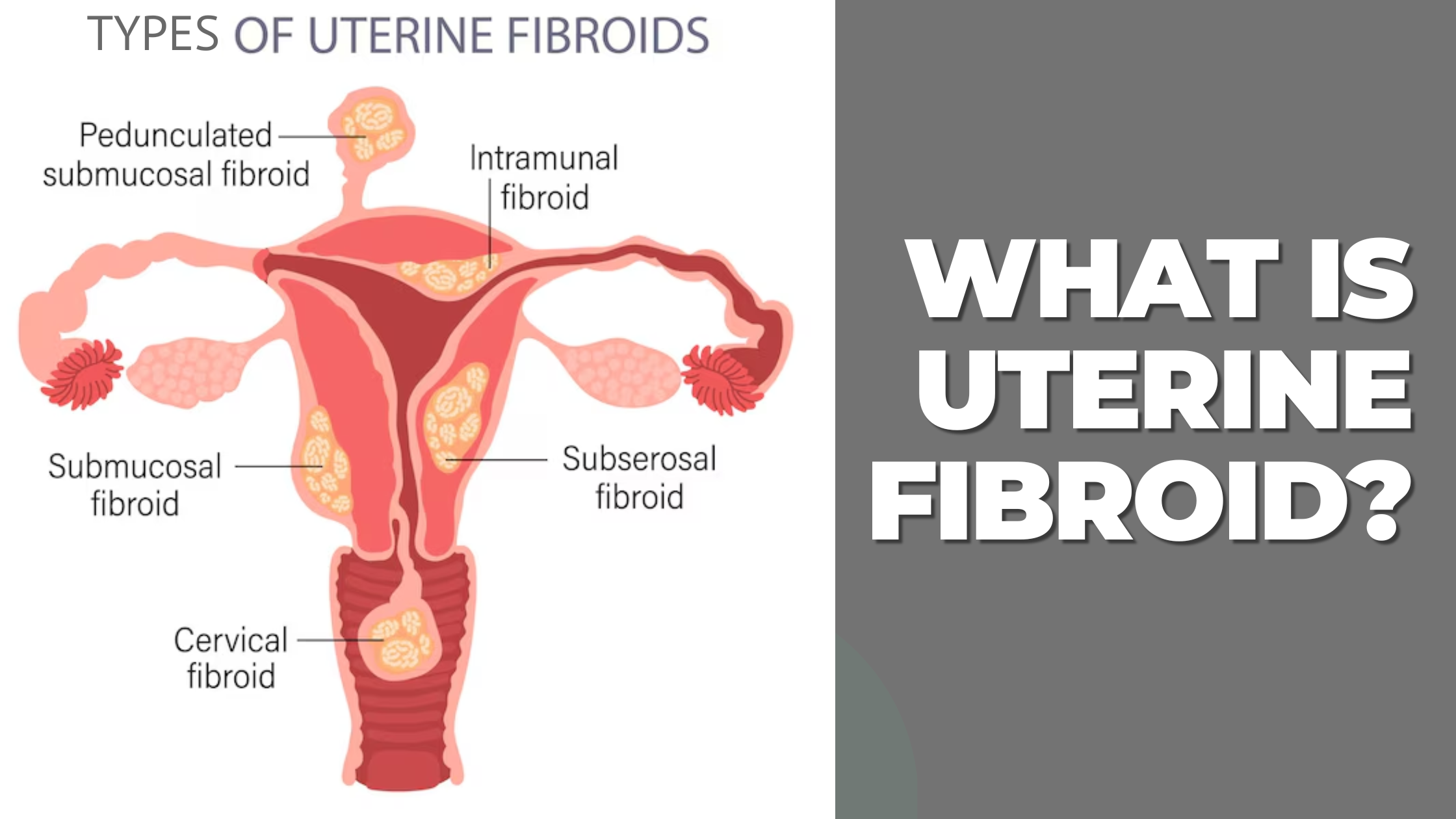
Types of fibroids
Intramural Fibroid: this is the most common type of fibroids. It is a non cancerous growth that develop within the muscular wall of the uterus.
Some of the characteristics are:
- It’s typically round and oval in shape
- They vary in size
- They may cause heavy menstrual bleeding
- They may cause prolonged bleeding
- They may sometimes cause the uterus to be enlarged and lead to noticeable abnormal bulge.
- They are majorly detected by ultrasound scan or pelvic exam
- It can also lead to pelvic pain
- Depending on the size, the treatment might range from monitoring to medication, it can finally lead to surgery.
Subserosal Fibroid: this occurs outside of the Uterus, and it leads to pressure on the surrounding organs. Like intramural Fibroid, subserosal varies from size to size. This type also causes discomfort especially when it presses towards another organ.
Some characteristic of subserosal Fibroid are:
- It varies in size
- Larger Fibroid can affect the bladder function, which can lead to regular urination
- It is usually recognized through ultrasound scan
- Many women with this fibroid can conceive without issues
- If the fibroid is asymptomatic, it may be monitored without opting for surgery
- Hormonal treatment can be used for monitoring
- Subserosal fibroid can lead to pain and discomfort
Submucosal fibroid: grows beneath the endometrium, which is the inner lining of the uterus. It varies in size. Submucosal is a type of fibroid that has characteristics such as:
- They often cause heavy and prolonged menstruation
- They can lead to irregular cycle
- Some women may experience pain during menstruation period
- It typically round and oval in shape
- Painful intercourse
- Abnormal swelling or bloating
- Constipation
Pedunculated fibroid: this type of fibroid grows on a peduncle, that is a stalk attached to the uterus. It is usually composed of smooth muscle and fibroid tissue. The characteristics are:
- Usually round and oval in shape
- It usually varies in size, and it can cause a twisting, leading to severe complications.
- Ultrasound scan is a treatment used to detect the fibroid
- Backache
- Constipation
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain
Types of pedunculated fibroid are: Intracavitary pedunculated fibroid, submucosal pedunculated fibroid, subserosal pedunculated fibroid.
Causes of Uterine fibroid
The exact cause of Uterine fibroid is yet to be fully understood. However, according to some research, certain factors that leads to the development are:
- Reproductive factors: this fibroid is more common for women between 30’s and 40’s. Fibroid usually grow during the reproductive year; it might shrink during menopause. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to the growth of fibroid. According to research, early onset of menstrual cycles has been linked to uterine fibroid.
- Environmental factor: Air and water pollution, lack of physical activities, stress, exposure pesticide, low fiber intake, chemical in plastic. Poor sleeping quality.
- Diet: high take if red meat and low intake of vegetables, fruit can also contribute to uterine fibroid.
- Genetic factor: if there’s history of fibroid, it increases the chance of one having it.
- Obesity: Excessive weight can influence the hormones; it can cause one to develop uterine fibroid.
Does fibroid cause infertility?
Uterine fibroid can cause infertility in many ways; some of the ways fibroid affects infertility are:
- Hormonal imbalance: fibroid can affect the hormones, thereby causing infertility. Hormonal imbalance happens when the body’s endocrine system produces too much or little hormone.
- Blockage of fallopian tube: large fibroid can cause a blockage in the fallopian tube, preventing sperm from entering the egg.
- Shape of Uterus: fibroid can destroy the shape of the uterus, making implantation of fertilized egg difficult.
- Cervical stenosis: this makes the sperm difficult to get to the uterus as a result of the narrowed cervical.
However, some women with fibroid still convince and have healthy babies.
Is Fibroid Cancerous?
Uterine fibroid is rarely cancerous. A large percentage of fibroid cancer seen are majorly non cancerous. However, there is a rare type of which is cancerous, it is referred to as Leiomyosarcomas. This type of fibroid has been proven to be seen in only one percent of women. Most fibroid are benign and do not increase cancer risk.
Characteristic of cancerous fibroid are
- Abnormal ultrasound
- Pain
- Rapid growth
- Unusual bleeding pattern
Furthermore, it is important to monitor fibroid for any change. Leiomyosarcomas are rare cancerous growth that develop into smooth muscle tissue if the uterus.
Which size of fibroid is dangerous?
The size of a fibroid alone does not necessarily determine its danger. However, larger fibroids generally those over 5 cm can lead to more significant symptoms, such as heavy bleeding, pain, or pressure on other.
Fibroid Sizes and Danger Levels are:
- Small: <2 cm (low risk)
- Medium: 2-5 cm (moderate risk)
- Large: 5-10 cm (high risk)
- Giant: >10 cm (severe risk)
There are various ways to detect the size of the fibroid. Example of the ways are as follows:
- Ultrasound scan
- CT scan
- Endometrial biopsy
- Pelvic examination
In addition, knowledge of fibroid size is important because it helps to know the kind of treatment required; monitoring the growth; symptom management.
Treatment for different fibroid size
- Small fibroid: most times, the requires watching, treatment might not be given immediately, however, some medicines such as birth control pill can be recommended.
- Medium fibroid: medications can be used to control it, surgical removal can also be done
- Large fibroid: surgical removal is considered, a non invasion treatment that uses ultrasound waves to shrink Fibroid can be done.
It is advisable to visit a health specialist to know the type of treatment that would be best for one’s condition.
Signs/ symptoms of Uterine fibroid
Common symptoms are:
- Constipation
- Back pain
- Leg pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Frequent urination
- Pelvic pain
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Painful sex
- Recurrent miscarriage
- Obesity
Rare symptoms:
- Bladder inflammation
- Abnormal virginal discharge
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Rectal pain
- Post menopause bleeding
- Acute pelvic pain
- Hemorrhage
- Abdominal tenderness
Like mentioned earlier, it is advisable to visit a health practitioner when these symptoms occur, however when severe symptoms occur such as: sudden change in symptoms, difficulty passing urine or stool, vaginal bleeding during period, if a woman shows any or two of three if these symptoms, it could be life threatening. It is advisable that when these occurs, she should visit the closest hospital immediately.
Risk factor of fibroid
The treatment of fibroids depends on their size, location, symptoms, and the patient’s overall health and preferences. The breakdown of the treatment are as follows
Medications:
Birth Control Pills: Help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce heavy bleeding.
GnRH Agonists: Reduce estrogen levels, shrinking fibroids temporarily; used for short-term management.
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain and discomfort.
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): Blocks blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
MRI-guided Focused Ultrasound: Uses ultrasound waves to heat and destroy fibroid tissue non-invasively.
Surgical option:
Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus; suitable for women who wish to maintain fertility.
Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus; recommended for severe symptoms or if fertility is not a concern.
General treatment:
Lifestyle Changes: Diet, exercise, and stress management may help reduce symptoms.
Difference between cyst and fibroid
Cysts occur on the ovaries, but can also develop on the uterus or other pelvic organs; Fibroids are growth within the uterine wall or attach to the outer layer.
Cyst are Fluid-filled sacs, often filled with liquid or semi-solid material, fibroid on the other hand are solid, non-cancerous growths made of muscle and fibrous tissue.
Cyst sizes are small (pea-sized) to large. Fibroids vary in size, from small (less than 1 cm) to large (over 10 cm).
Difference in cyst symptoms and fibroid
Cysts:
- Pelvic pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Heavy bleeding
- Infertility
Fibroids:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pressure
- Abdominal swelling
- Painful intercourse
Causes of cyst are
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Genetic
- Infection
- Menstrual irregularities
- Estrogen imbalance
Treatment for cyst is
- Watchful waiting
- Hormonal therapies
- Surgery (cyst removal)
- Drainage
Impact of cyst on fertility
- May affect ovulation
- May cause endometriosis with can cause infertility
- Ovarian damage
Cysts can grow rapidly or remain stable in size.
Can uterine fibroid lead to sudden death?
Uterine fibroid can lead to death if not well taken care of. Severe bleeding can lead to shock or death. Fibroid increases risk of pregnancy which can life threatening. Fibroid can compress the intestine leading to bowel obstruction. Chronic bleeding can cause health failure or respiratory failure with cancer lead to sudden death. Postpartum hemorrhage can cause excessive bleeding after childbirth which can be life threatening.
Conclusion
Educating oneself about fibroid is the first step to have proper control of the body. In this article is highlighted the significance of Uterine fibroid as a major public health concern, emphasizing the need for education and increased awareness. As researches are done, it is necessary to translate evidence-based practices into clinical settings, ensuring that women receive effective and compassionate care.